All About Clearing Ponds Of Weeds
A Biased View of Clearing Ponds Of Weeds
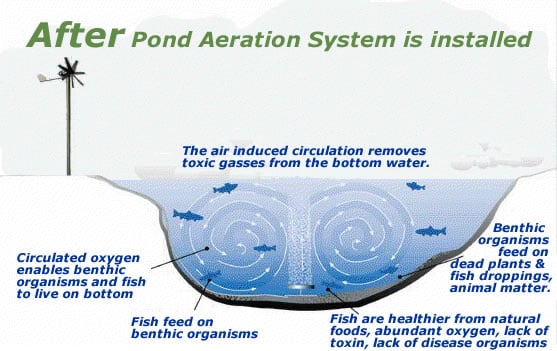 Getting The How To Aerate Water Without Electricity To Work
Getting The How To Aerate Water Without Electricity To Work
Sunshine is likewise extremely essential to facultative lagoons due to the fact that it contributes to the development of green algae on the water surface area. Because algae are plants, they require sunshine for photosynthesis. Oxygen is a by-product of photosynthesis, and the presence of green algae contributes substantially to the amount of oxygen in the aerobic zone.
The oxygen in the aerobic zone makes conditions favorable for aerobic germs. Both aerobic and anaerobic germs are very important to the wastewater treatment procedure and to each other. Germs treat wastewater by converting it into other compounds. Aerobic germs convert wastes into carbon dioxide, ammonia, and phosphates, which, in turn, are utilized by the algae as food.
Top Guidelines Of Demucking Pond
Many of these spin-offs are then utilized as food by both the aerobic germs and algae in the layers above. In addition, the sludge layer at the bottom of the lagoon has plenty of anaerobic bacteria, sludge worms, and other organisms, which provide treatment through food digestion and prevent the sludge from rapidly building up to the point where it needs to be gotten rid of.
Sludge in all lagoons accumulates quicker in cold than in warm temperatures. However, lots of facultative lagoons are designed to function well without sludge elimination for 5 to ten years or more. Lagoons need to be designed by qualified professionals who have had experience with them. License requirements and regulations worrying aspects of lagoon style differ, but there are some design issues common to all lagoons.
Dredging A Small Lake Can Be Fun For Anyone
have laws concerning the siting of lagoons, including their range from groundwater below, and their range from homes and businesses - milfoil infestation. Lagoons likewise need to lie downgrade and downwind from the homes they serve, when possible, to prevent the additional cost of pumping the wastewater uphill and to prevent smells from becoming an annoyance.
Any obstructions to wind or sunshine, such as trees or surrounding hillsides need to be thought about. Trees and weed growth around lagoons ought to be managed for the very same factors. In addition, water from surface area drainage or storm overflow need to be kept out of lagoons, if essential install diversion terraces or drains above the site.
What Is Aeration Water Treatment for Dummies
The size and shape of lagoons is created to make the most of the amount of time the wastewater remains in the lagoon. Detention time is generally the most important aspect in treatment. In general, facultative lagoons require about one acre for every 50 homes or every 200 individuals they serve. Oxygenated lagoons deal with wastewater more effectively, so they tend to require anywhere from one-third to one-tenth less land than facultative lagoons.
Lagoons can be round, square, or rectangular with rounded corners. Their length ought to not surpass 3 times their width, and their banks ought to have outdoors slopes of about three units horizontal to one unit vertical. This moderate slope makes the banks simpler to cut and keep. In systems that have dikes separating lagoon cells, dikes likewise ought to be simple to preserve.
Things about Algae Chemicals
The bottoms of lagoons should be as flat and level as possible (other than around the inlet) to facilitate the continuous circulation of the wastewater. Keeping the corners of lagoons rounded likewise assists to maintain the overall hydraulic pattern in the lagoons and prevents dead areas in the flow, called short-circuiting, which can affect treatment.
Partial-mix aerated lagoons are typically designed to be much deeper than facultative lagoons to enable space for sludge to choose the bottom and rest undisturbed by the rough conditions produced by the aeration process. Wastewater gets in and leaves the lagoon through inlet and outlet pipelines. Modern develops place the inlet as far as possible from the outlet, on opposite ends of the lagoons, to increase detention times and to prevent short-circuiting.
The Best Strategy To Use For Dredging A Small Lake
Outlets are developed depending on the approach of discharge. They often include structures that permit the water level to be raised and reduced. Aerators, which are utilized rather of algae as the main source of oxygen in oxygenated lagoons, work by launching air into the lagoon or by upseting the water so that air from the surface is mixed in (barley algae control).
 Getting The How To Clean Natural Pond To Work
Getting The How To Clean Natural Pond To Work
Different aerator styles produce either great or coarse bubbles, and work either on the water surface area or submerged. Subsurface aerators are more effective in climates where the lagoon is most likely to be covered by ice for part of the year. Lagoons can draw in kids, family pets, and unwary adults, who may think they appear like great locations to play and even swim.
An Unbiased View of How To Aerate Water Without Electricity
Safety training must be offered for property owners, operators, and anybody else dealing with these systems. Laws in the majority of locations need lagoons to be surrounded by high fences with locking gates and have indication plainly published. One of the advantages of lagoons is that they require less staff hours to run and maintain than a lot of other systems.
Routine assessments, screening, record keeping, and maintenance are required by local and state companies, and are all required to make sure that lagoons continue to offer excellent treatment. How frequently lagoons should be checked depends on the type of lagoon, how well it functions, and regional and state requirements. Some lagoons need more frequent checking in the spring and summer season, when lawn and weeds grow rapidly and when seasonal rental residential or commercial properties are inhabited.
Some Known Factual Statements About Dredging A Small Lake
Among the most essential signs are biochemical oxygen need (BODY) and total suspended solids (TSS). Body is very important since it measures how much oxygen organisms in the wastewater would consume when released to receiving waters. TSS determines the amount of solid materials in http://ricardogege541.lowescouponn.com/the-20-second-trick-for-clearing-ponds-of-weeds the wastewater. If body or TSS levels in the effluent are too expensive, they can break down the quality of getting waters (how to fix lake Okeechobee).
But because lagoon conditions alter continuously, the majority of tests need to be carried out numerous times, and in some cases at specific intervals or times of the day, to get a precise general view of the lagoon's health. Operators can be trained to take samples and carry out some or all of the tests themselves. It is normally more useful for part-time operators of small systems to send out samples out to a laboratory to be evaluated - how to clean a lake - water aeration system.
The Single Strategy To Use For How To Get Rid Of Duckweed In A Lake
These weeds use up valuable area that should be occupied by algae, they can stop sunshine from penetrating the wastewater, and sluggish blending by the wind. Scum that collects on the water surface ought to be removed for the same reasons as duckweed, but also to control odors and pests and to avoid inlet and outlet obstructing. kill pond weeds naturally.
Finally, the depth of the sludge layer in lagoons must be checked at least as soon as each year, generally from a boat using a long stick or hollow tube. In a lot of lagoon systems, sludge eventually accumulates to a point it should be gotten rid of, although this may take years. Efficiency will suffer if excessive sludge is allowed to accumulate.
Not known Facts About How To Aerate Water Naturally
Duckweed, watermeal, and hyacinth that grow on the water surface ought to be physically gotten rid of, often from a boat with a tool, like a rake or skimmer. Blue-green algae-Unlike green algae, this alga is stringy and can clump, block sunlight, and trigger short-circuiting. It can control lagoons when conditions are bad, when p, H is low, or when protozoa eat all of the green algae.
"Lagoons were an improvement then, and they still work well today." Found on Flathead Lake in northwest Montana, the city was integrated in 1910 and has actually experienced sluggish, constant development for many years. Just recently, the growth rate has actually increased to about five percent annually, bringing the current population to about 4,300.
The How Does Aeration Clean Water Statements
 How To Clean Natural Pond Fundamentals Explained
How To Clean Natural Pond Fundamentals Explained
Circulations were simply diverted from one lagoon to the other every six months. To accommodate growth, the city constructed a new system in 1981 with three aerated lagoons and one polishing lagoon. Polson also started to run its own lab to keep track of the system (aeration in water treatment). "We picked the oxygenated system based upon recommendations
Welkom bij
Beter HBO
© 2025 Gemaakt door Beter HBO.
Verzorgd door
![]()
Je moet lid zijn van Beter HBO om reacties te kunnen toevoegen!
Wordt lid van Beter HBO